Do you know which appliances use the most electricity in your home? Knowing which appliances in your home consume the most electricity can help you understand the power consumption needs when planning for an emergency backup power system.
When planning for a backup power system, it is important to know the wattage requirements of your household items you want to power when the electrical grid goes down.
So how many watts do common household appliances use? This quick reference guide will show you which appliances use the most electricity, and how to find out how many watts an appliance uses.
Don’t forget to inspect each appliance in your home individually to see the actual wattage consumption numbers.
Small Appliances Estimated Wattage
| Appliance | Running Wattage | Starting Watts |
|---|---|---|
| Air Fryer | 1500 W | 0 |
| Air Purifier | 25 W | 0 |
| Aquarium | 50-1000 W | 0 |
| Blender | 300-1000 W | 0 |
| Clothes Iron | 1000-1500 W | 0 |
| Electric Skillet | 1000-1500 W | 0 |
| Espresso Coffee Machine | 1300 W | 200 W |
| Hot Plate | 750-1500 W | 0 |
| Clothes Iron | 1000-1500 W | 0 |
| Keurig | 200-400 W | 1500 W |
| Microwave (600-1200 watt cooking power) | 1000-2000 W | 0 |
| Rice Cooker | 200 W | 500 W |
| Slow Cooker | 160 W | 20 W |
| Space Heater | 750-1500 W | 0 |
| Toaster | 800-1500 W | 0 |
| Toaster Oven | 1200 W | 0 |
| Waffle Iron | 800-1500 W | 0 |
| Wine Cooler | 83 W | 0 |
Major Appliances Estimated Wattage
| Appliance | Running Wattage | Starting Watts |
|---|---|---|
| Central AC (10,000 BTU) | 1500 W | 4500 W |
| Central AC (24,000 BTU) | 3800 W | 4500 W |
| Central AC (40,000 BTU) | 6000 W | 6700 W |
| Chest Freezer | 600 | 2200 W |
| Clothes Dryer (Electric) | 5400 W | 6750 W |
| Clothes Dryer (Gas) | 700 W | 1800 W |
| Dehumidifier | 240 W | 0 W |
| Dishwasher | 1200-2400 W | 1500 W |
| Electric Oven | 2150 W | 0 W |
| Electric Stove | 2000-5000 W | 0 W |
| Furnace Fan | 750-1200 W | 2350 W |
| Household Fan | 50-120 | 10-15 W |
| Refrigerator | 500-750 W | 2200 W |
| Smart Home Thermostat | 24 W | 0 W |
| Space Heater | 750-1500 W | 0 W |
| Sump Pump 1/2 hp | 1050 W | 2150 W |
| Sump Pump 1/3 hp | 800 W | 1300 W |
| Thermostat | 360 W | 0 |
| Washing Machine | 500-1200 W | 2300 W |
| Well Pump 1/2 hp | 1000 W | 2100-4000 W |
| Well Pump 1/3 hp | 750 W | 1400-3000 W |
What is Running Watts?
Running or rated watts are the continuous watts needed to keep an appliance running. It’s the work over time necessary to keep its momentum from falling.
What is Starting Watts?
Starting watts are the wattage needed to get a device running. A generator can provide this power temporarily,surge power and it’s also called peak or surge power. This is why starting/surging measurements vary greatly depending on how long they’re used at full capacity before shutting off again.
How to Calculate the Wattage of your Appliances?
The first step to finding your appliance’s wattage is by looking for the manufacturers label. All appliances that require electric power by law require a manufacturers label.
Once you have the manufacturers Amp requirements in hand, use this conversion formula:
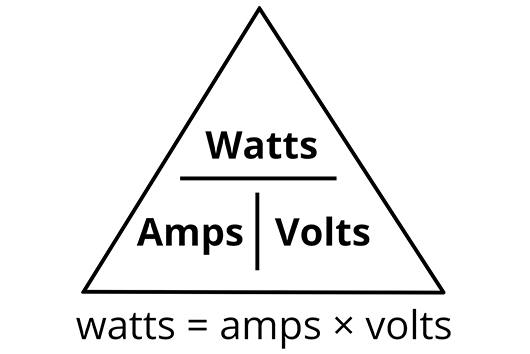
Power = Amps × Voltage
As an example, to find the wattage of appliance that requires 20 amps at 120 volts:
- 20A × 120V = 2400 Watts are required to power the appliance
However, also be sure to factor in the starting watts. Lasting on 3 to 5 seconds, starting wattage is the biggest draw on the portable generator.
Conclusion: How many watts do common household appliances use
Electricity is a necessary part of life and we should all be prepared for when it goes out. The knowledge that you’ve gained from this quick reference guide will help you plan your emergency backup power system.
Remember, your appliances are designed to operate on a specific wattage, so even during an outage you can still use them safely.
In an effort to be the most comprehensive resource on appliance power requirements, we will add and update this list regularly.





